Scoliosis in Children and Teens: When to Seek Help
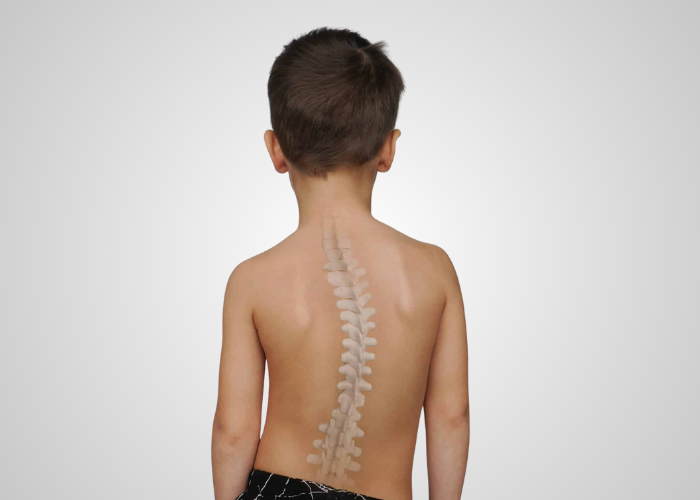
What is Scoliosis in Children and Teens?
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves sideways, forming an "S" or "C" shape. While it can affect individuals of any age, it is most commonly diagnosed during childhood and adolescence, particularly during growth spurts. Scoliosis in children is often subtle at first, with parents noticing signs like uneven shoulders, a tilted hip, or a posture that leans to one side.
The exact cause of scoliosis is often unknown (idiopathic), but it can also result from neuromuscular conditions, birth defects, or spinal injuries. The condition can develop slowly and worsen over time if left untreated, leading to more severe curvature and complications.
Symptoms of Pediatric Scoliosis
While scoliosis can develop silently, there are several signs to watch for in children and teens:
Uneven Shoulders: One shoulder may appear higher than the other.
Uneven Hips: One hip may be higher than the other, or one side of the body may stick out more than the other.
Leaning Posture: The child may appear to lean to one side, or their head may not align with their body.
Back Pain: While not always present in mild cases, some children may experience back pain or discomfort as the curvature progresses.
It's important to note that scoliosis may not cause any noticeable pain or discomfort early on, which is why regular screenings and physical exams are essential for early detection.
Diagnosis of Scoliosis in Children
The diagnosis of scoliosis typically begins with a physical examination, where the doctor looks for signs such as uneven shoulders, hips, or posture. If scoliosis is suspected, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs are used to evaluate the severity of the curvature and to determine whether the spine is still growing.
The degree of curvature is measured in degrees, and scoliosis is classified as follows:
Mild Scoliosis: Curvature of less than 25 degrees
Moderate Scoliosis: Curvature between 25 and 45 degrees
Severe Scoliosis: Curvature greater than 45 degrees
The doctor will also consider the child's age, growth potential, and the likelihood of the curvature worsening over time when deciding on the appropriate course of treatment.
At our Mumbai Institute of Spine Surgery (M.I.S.S), we use advanced diagnostic techniques to ensure accurate assessment of pediatric scoliosis cases.
Treatment Options for Pediatric Scoliosis
The treatment for scoliosis in children and teens depends on the severity of the curve and the child's age. Treatment options include:
Observation and Exercises: In mild cases, the doctor may recommend observation and regular follow-ups to monitor the condition. Physical therapy may be used to strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve posture.
Bracing: For moderate scoliosis, especially if the child is still growing, a brace may be prescribed to prevent further progression of the curve. Braces are custom-fitted to the child and worn throughout the day, except during activities like bathing or swimming.
Surgical Intervention: In more severe cases or if the curvature is rapidly progressing, surgery may be required. The goal of surgery is to correct the spine's curvature and prevent future complications, such as breathing problems or postural deformities.
Minimally Invasive Surgery: This modern approach to scoliosis surgery involves smaller incisions, which results in faster recovery times, less pain, and minimal scarring. The surgery uses advanced imaging technology for greater precision.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery: With robotic-assisted navigation, surgeons can achieve even greater accuracy in correcting the spine. Using 3D imaging and custom 3D-printed implants, the surgery can be tailored to the individual needs of the child, ensuring optimal results and reduced risk of complications.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery for Children
Minimally invasive scoliosis surgery offers significant advantages over traditional open surgery, especially for children and teens:
Smaller Incisions: The surgery is performed with small incisions, which leads to less trauma to the body.
Faster Recovery: Children typically experience quicker recovery times, allowing them to return to their normal activities sooner.
Reduced Pain: The minimally invasive technique reduces post-surgical pain, making the recovery process more comfortable.
Better Precision: Robotic-assisted navigation and advanced imaging allow for highly precise adjustments to the spine, leading to better long-term results.
Top Hospitals for Pediatric Scoliosis Treatment in India
Children and teens from across India, including Mumbai, Delhi, Pune, Nashik, Thane, Navi Mumbai, Raipur, Indore, Bhopal, and Jaipur, can receive world-class scoliosis care at leading hospitals such as:
Lilavati Hospital
Bombay Hospital
Breach Candy Hospital
Saifee Hospital
These hospitals are equipped with the latest technology and offer a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to scoliosis treatment.
Our Centre of Excellence in Spine Surgery (C.E.S.S) provides comprehensive care for pediatric spine conditions including scoliosis.
Why Choose Dr. Vishal Kundnani for Pediatric Scoliosis Treatment?
Dr. Vishal Kundnani, Director and Head of Spine Services at Lilavati and Bombay Hospitals, is a recognized expert in the treatment of scoliosis. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Kundnani specializes in minimally invasive and robotic-assisted scoliosis surgeries, ensuring the best possible outcomes for children and teens. He is dedicated to providing personalized, patient-centered care that meets the unique needs of each young patient.
Learn more about our spine team and their expertise in treating various spine conditions including herniated disc, spinal stenosis, and spondylolisthesis.
Schedule Your Consultation with Dr. Vishal Kundnani
If you notice any signs of scoliosis in your child or teen, don't wait to seek professional help. Early treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and ensure the best possible outcome.
📞 Call: 9619100123, 9619200123, 9619300123 to consult Dr. Vishal Kundnani, the best scoliosis surgeon in Mumbai and India.
Visit our contact page for more information or to schedule an appointment. You can also explore our patient testimonials and case studies to learn about successful pediatric scoliosis treatments.




